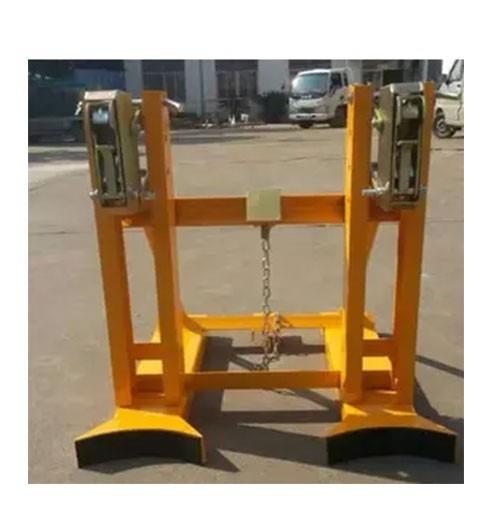
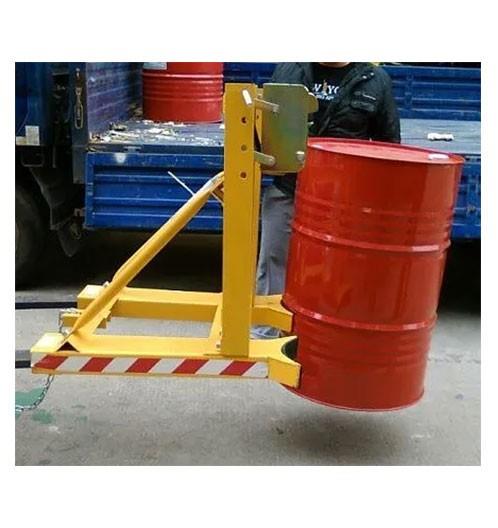
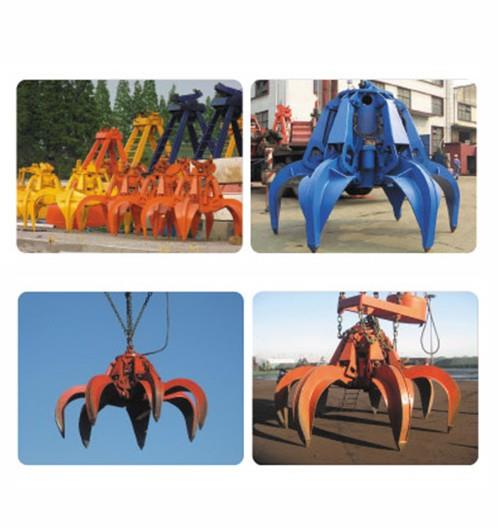
産(chǎn)品簡(jiǎn)介:
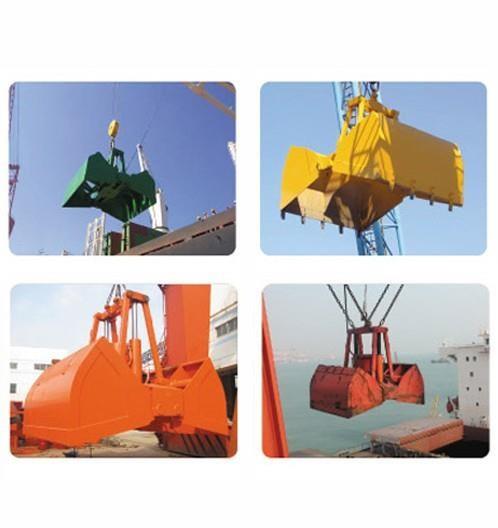
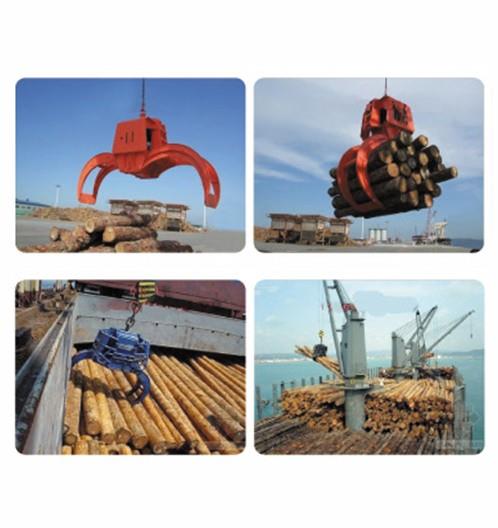
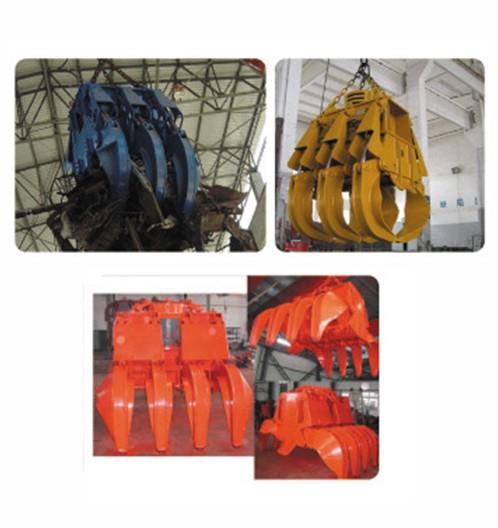
the most commonly used lifting appliance is the hook, and others include lifting rings, lifting suction cups, clamps and lifting beams. lifting suction cups, clamps and lifting beams can be used as special lifting appliances on cranes for a long time, and can also be used as replaceable auxiliary lifting appliances hanging on hooks for temporary use. they are commonly used in multi cargo warehouses and storage yards to improve operation efficiency. the lifting appliance for grabbing bulk materials is generally a grab with jaw plate that can be opened and closed, and electromagnetic suction cups can also be used to absorb magnetic materials such as metal chips. the commonly used lifting appliances for lifting liquid materials are buckets and buckets. generally, the molten steel or chemical solution is discharged by tilting or bottom plug, and the liquid materials such as concrete are discharged by opening the bottom door of the bucket.